Medications that we use, whether they are common treatments or more specialized ones, have all been discovered because of research. For example, clinical research allowed developing drugs used for the treatment of cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, etc. It takes about 15 years for researchers to develop a treatment that is safe and effective for each disease (see picture).
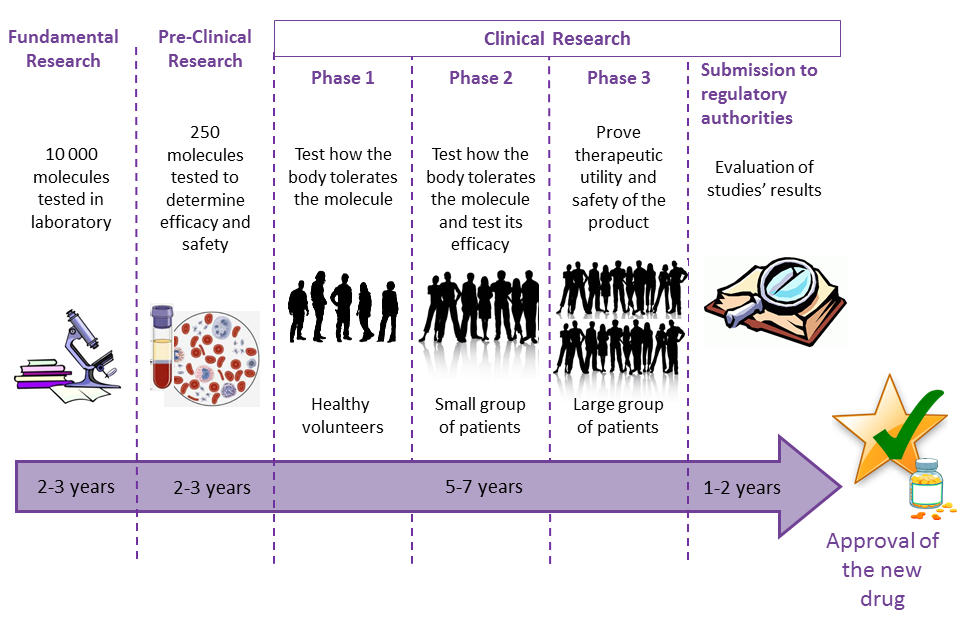
The different steps of medication development and research
Clinical research relies on results of fundamental research to develop new treatments, devices and medical acts, and to evaluate their efficacy. In pre-clinical phases, the research is performed in university or pharmaceutical laboratories, on biological models (in-vitro testing) or on animal models (in-vivo testing). The objective is to identify new molecules to safely and effectively use them later in humans. When researchers believe they have found an efficient treatment, it is time for the clinical research steps.
Unknown to the great public, clinical research represents a major stake for our health. Indeed, it is a crucial step in the development of new treatments and innovative medications. It is to be noted that clinical research is strictly regulated by laws and can only take place in precise conditions.
A clinical study consists in testing a medication, a medical device, or a medical act on humans to evaluate which benefits it has and which risks it entails. A clinical trial can also evaluate an already existing treatment in order to improve it or compare it with another treatment. A clinical study is one of the last steps in the development of a new treatment.
Medical research contributes to the discovery of new treatments and to the improvement of the knowledge of diseases. 3 phases of clinical studies are necessary for a new medication to be approved for the treatment of a disease:
• Phase 1 aims to evaluate the tolerance of the organism to the molecule. It is performed on small groups of participants, in general healthy volunteers, i.e. people that do not suffer from the disease for which the molecule is tested.
• Phase 2 aims to evaluate the tolerance and the efficacy of the molecule. It is performed on small groups of participants suffering from the disease to be treated. In general, it takes place in hospitals in order to ensure close medical surveillance of the participants.
• Phase 3 aims to prove the therapeutic interest of the tested product and the absence of its harmfulness. It is conducted on a large number of ill participants up to thousands of participants. This phase constitutes the last step before a medication is available to patients.
Before it can start, each clinical study is submitted to regulatory authorities in the country where it will be conducted. The authority approval is mandatory to perform the study. In addition, it is evaluated by an ethics committee whose role is to ensure that the protocol respects the safety of participants, and the rules and laws of clinical research. It takes into account, among other things, the relevance of the study, the relation between the study objectives and the means deployed, as well as the quality of the information delivered to the people who will participate when obtaining their consent. The ethics committees are composed of healthcare professionals, members of the collectivity, ethics representatives, legal representatives and of any other person that possesses a precise expertise. An ethics committee approval is mandatory to initiate a clinical study.
Participation to clinical studies is voluntary and it is always possible to withdraw the consent to participate on simple verbal notice, without any prejudice. Although clinical research participation is potentially open to everyone, each clinical trial has specific inclusion and exclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria describe the characteristics that participants must display, whereas the exclusion criteria describe the characteristics that participants must not display to participate in the clinical study. When you participate in a clinical project, you are given, at your first visit, a patient ID number, so it is impossible to identify you. Your confidentiality is then protected.
Clinical studies participants are major actors in the success of medical research. There are no direct benefits guaranteed to you because of your participation to a study. However, if the treatment is deemed efficient, it will help the progress of scientific knowledge in this field.
In 2000, 25% of deaths were attributable to cardiac diseases in Canada. This percentage has decreased to 20% in 2011. This improvement is attributable, among other things, to the medical research performed in the past years.
